Neuroscience
(2014) Regulatory mechanisms underlying the differential growth of dendrites and axons
Media:2014_--_Regulatory_mechanisms_underlying_the_differential_growth_of_dendrites_and_axons.pdf
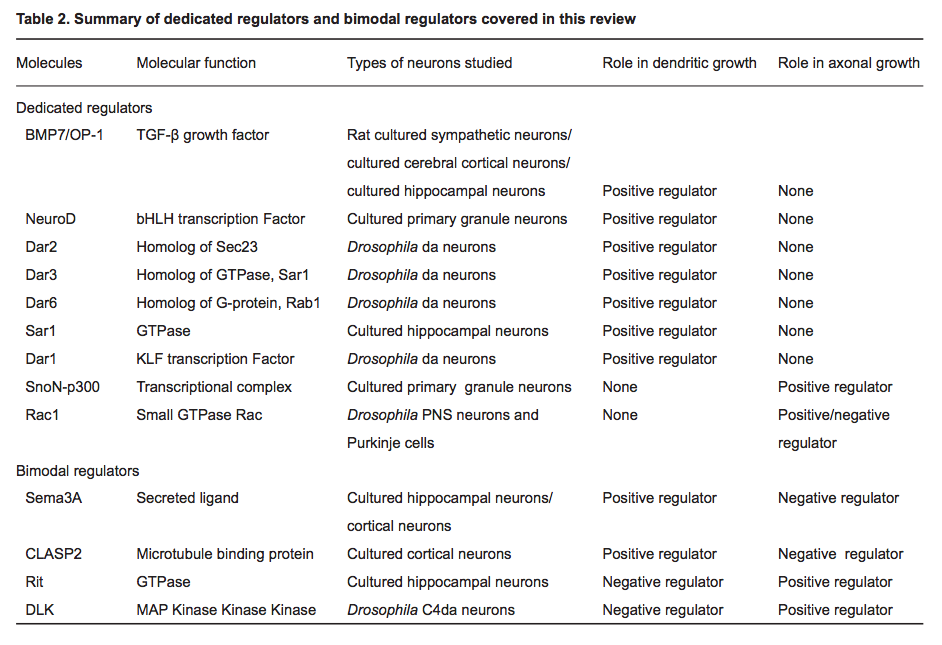
- "Recent studies have uncovered two distinct types of regulatory mechanisms that differentiate dendritic and axonal growth: dedicated mechanisms and bimodal mechanisms. Dedicated mechanisms regulate either dendrite- specific or axon-specific growth; in contrast, bimodal mechanisms direct dendritic and axonal development in opposite manners."
Sema3A is where???
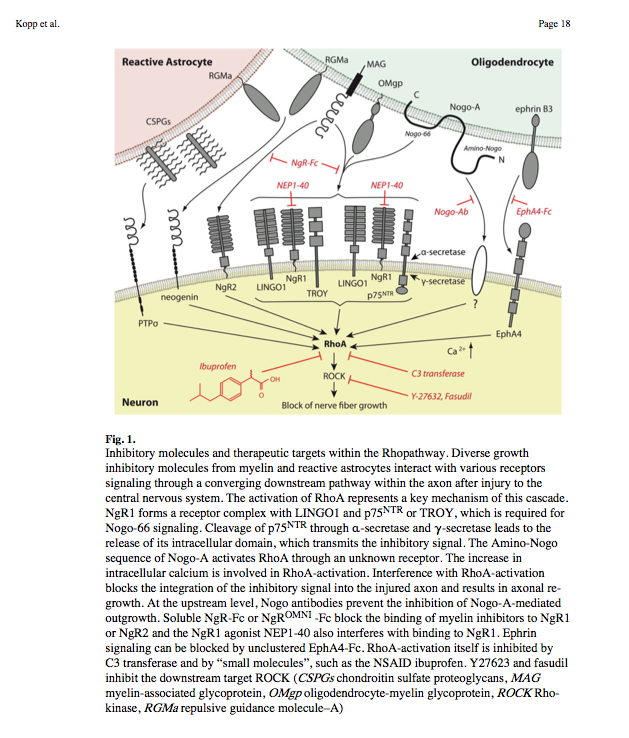
[www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3744771/ Small-molecule-induced Rho-inhibition: NSAIDs after spinal cord injury]
(2005) Local translation of RhoA regulates growth cone collapse
- Neuronal development requires highly coordinated regulation of the cytoskeleton within the developing axon. This dynamic regulation manifests itself in axonal branching, turning and pathfinding, presynaptic differentiation, and growth cone collapse and extension. Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A), a secreted guidance cue that primarily functions to repel axons from inappropriate targets, induces cytoskeletal rearrangements that result in growth cone collapse1. These effects require intra-axonal messenger RNA translation. Here we show that transcripts for RhoA, a small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) that regulates the actin cytoskeleton, are localized to developing axons and growth cones, and this localization is mediated by an axonal targeting element located in the RhoA 3' untranslated region (UTR). Sema3A induces intra-axonal translation of RhoA mRNA, and this local translation of RhoA is necessary and sufficient for Sema3A-mediated growth cone collapse. These studies indicate that local RhoA translation regulates the neuronal cytoskeleton and identify a new mechanism for the regulation of RhoA signalling.
[www.jneurosci.org/content/32/41/14442.full.pdf Intra-Axonal Translation of RhoA Promotes Axon GrowthInhibition by CSPG]
- RhoA transcripts have been detected in axons of embryonic dorsal root ganglia (DRG), retinal ganglion, and cortical and hippocampal neurons, and are locally translated in DRG axons in response to the inhibitory guidance cue Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A) and mediate growth cone collapse (Wu et al., 2005).
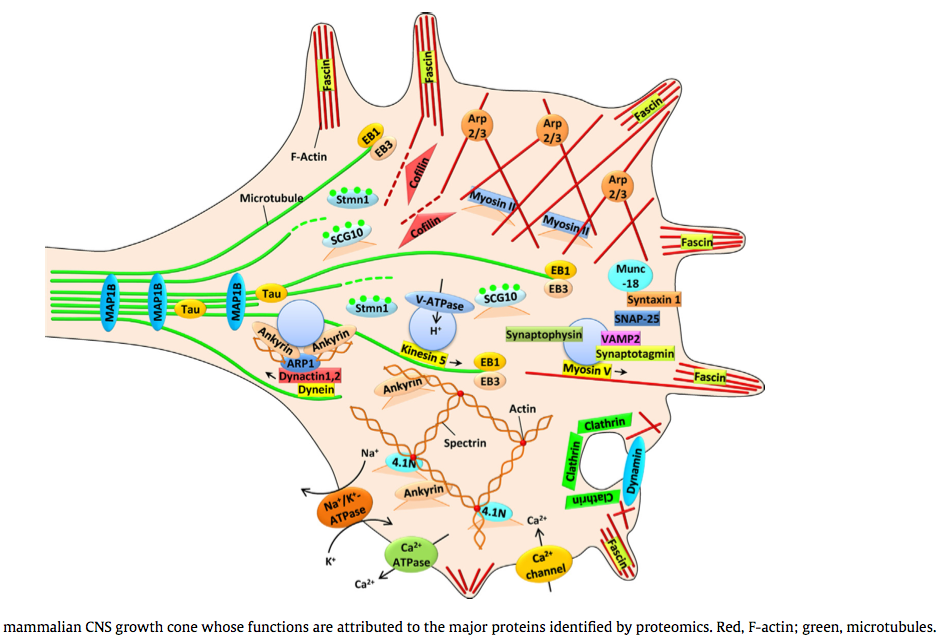
(2014) Proteomic identification of the molecular basis of mammalian CNS growth cones
Media:2014_--_Proteomic_identification_of_the_molecular_basis_of_mammalian_CNS_growth_cones.pdf
Shrooms
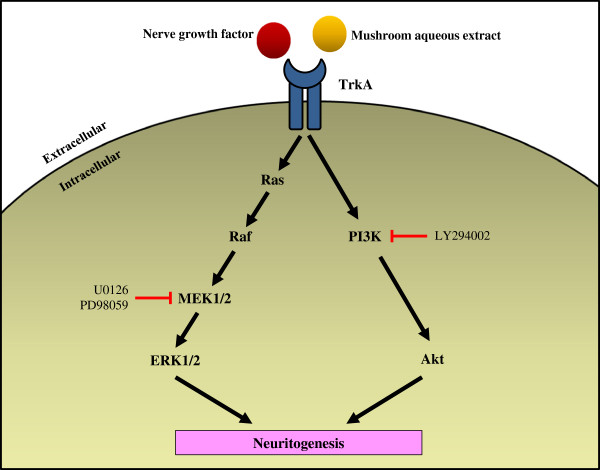
Potentiation of neuritogenic activity of medicinal mushrooms in rat pheochromocytoma cells
DIHEXA
Ashwagandha
Axon (or dendrite) predominant outgrowth induced by constituents from Ashwagandha
- "results suggest that axons are predominantly extended by withanolide A, and dendrites by withanosides IVand VI."
Media:2002_--_Axon-_or_dendrite-predominant_outgrowth_induced_by_constituents_from_Ashwagandha.pdf
- withanoside IV a.k.a. Sominone = GDNF-independent stimulator of the RET pathway and/or a novel modulator of RET signalling
[1]