Difference between revisions of "Machine Learning"
(→Misc) |
(→RL) |
||
| (84 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [https://github.com/songrotek/Deep-Learning-Papers-Reading-Roadmap/blob/master/README.md Deep Learning Papers Reading Roadmap] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Communities == | ||
| + | IRC FreeNode: ##machinelearning | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gitter: https://medium.freecodecamp.com/best-gitter-channels-for-data-science-machine-learning-6e8eeb5063c0#.5pfx3ho2q | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Getting Started == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLjJh1vlSEYgvZ3ze_4pxKHNh1g5PId36- DeepLearning.TV YouTube playlist] -- good starter! | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://keras.io/ Keras] runs on top of TensorFlow or Theano | ||
| + | |||
== Tuts == | == Tuts == | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://brohrer.github.io/how_bayesian_inference_works.html <-- good ML vids too | ||
| + | |||
[http://ufldl.stanford.edu/tutorial/ UFLDL Stanford (Deep Learning) Tutorial] | [http://ufldl.stanford.edu/tutorial/ UFLDL Stanford (Deep Learning) Tutorial] | ||
| − | [http://home.agh.edu.pl/~vlsi/AI/backp_t_en/backprop.html Principles of training multi-layer neural network using backpropagation] <-- Great visual guide! | + | [http://home.agh.edu.pl/~vlsi/AI/backp_t_en/backprop.html Principles of training multi-layer neural network using backpropagation] <-- Great visual guide! |
| + | http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/ <-- Python code here (Theano) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''(Coursera) Neural Networks for Machine Learning — Hinton''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | - [http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/ Hinton's homepage] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
- [https://www.coursera.org/learn/neural-networks Coursera course] | - [https://www.coursera.org/learn/neural-networks Coursera course] | ||
| − | |||
- [https://www.coursetalk.com/providers/coursera/courses/neural-networks-for-machine-learning Intro vid for course] | - [https://www.coursetalk.com/providers/coursera/courses/neural-networks-for-machine-learning Intro vid for course] | ||
| − | - [ | + | - [https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLoRl3Ht4JOcdU872GhiYWf6jwrk_SNhz9 Vids (on YouTube)] |
| + | - [https://www.youtube.com/user/aicourses/playlists?view=50&flow=list&shelf_id=2 same, better organized] | ||
| + | |||
- [https://www.norsys.com/tutorials/netica/secA/tut_A1.htm Bayesian Nets Tutorial] -- helpful for later parts of Hinton | - [https://www.norsys.com/tutorials/netica/secA/tut_A1.htm Bayesian Nets Tutorial] -- helpful for later parts of Hinton | ||
| + | |||
| + | Code: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - https://github.com/bpjsincl/coursera-neural-net <-- Python | ||
| + | - https://github.com/BradNeuberg/hinton-coursera <-- MatLab | ||
| + | - https://github.com/davidandrzej/py-coursera-neural <-- no good | ||
| + | - https://github.com/Sohojoe/hinton-coursera <-- fork of the Matlab | ||
| + | |||
| + | - https://github.com/mdenil/dropout | ||
| + | |||
| + | - http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/code.html <-- Boltzmann stuff MATLAB Ruslan Salakhutdinov and Geoff Hinton | ||
| + | - https://github.com/echen/restricted-boltzmann-machines Python RBM NICE | ||
| + | - http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/rbm.html | ||
| + | - http://deeplearning4j.org/restrictedboltzmannmachine.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | - [https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/science.pdf Hinton, Salakhutdinov (2006) -- Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks] <-- Stacked RBM AutoEncoders (DBM) + CODE! | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Exercises: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - https://www.reddit.com/r/MachineLearning/comments/1wgleb/where_can_i_find_the_exercises_to_the_coursera_ml/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Other courses == | ||
[https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLE6Wd9FR--EfW8dtjAuPoTuPcqmOV53Fu Deep learning at Oxford 2015 (Nando de Freitas)] | [https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLE6Wd9FR--EfW8dtjAuPoTuPcqmOV53Fu Deep learning at Oxford 2015 (Nando de Freitas)] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 63: | ||
[http://www.holehouse.org/mlclass/ Notes] for Andrew Ng's Coursera course. | [http://www.holehouse.org/mlclass/ Notes] for Andrew Ng's Coursera course. | ||
| − | + | [https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL6Xpj9I5qXYEcOhn7TqghAJ6NAPrNmUBH Hugo Larochelle: Neural networks class - Université de Sherbrooke] [http://info.usherbrooke.ca/hlarochelle/neural_networks/content.html RESOURCES] | |
| − | [ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCPk8m_r6fkUSYmvgCBwq-sw/playlists Karpathy -- CS231n]: course [http://cs231n.github.io/ here], http://karpathy.github.io/neuralnets/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | == RL == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www0.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/d.silver/web/Teaching.html David Silver's RL course] [https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLMZdRRhAoLnKFxZlmFoFp0uHVvN2PSE9T YouTube playlist] | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://rll.berkeley.edu/deeprlcourse/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-best-books-about-reinforcement-learning | ||
== Books == | == Books == | ||
[http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html Nielsen -- Neural Networks and Deep Learning] <-- online book | [http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html Nielsen -- Neural Networks and Deep Learning] <-- online book | ||
| − | [http://www.deeplearningbook.org/ http:// | + | [http://www.deeplearningbook.org/ deeplearningbook.org] [https://github.com/HFTrader/DeepLearningBook pdf] |
| + | |||
| + | [https://page.mi.fu-berlin.de/rojas/neural/ Rojas (1996) -- Neural Networks - A Systematic Introduction] ??? | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://statweb.stanford.edu/~tibs/ElemStatLearn/ The Elements of Statistical Learning] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Book-like Papers: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.07800 On the Origin of Deep Learning] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://arxiv.org/abs/1404.7828 Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Trading == | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://quantopian.com/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | (2013) [http://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2013/TakeuchiLee-ApplyingDeepLearningToEnhanceMomentumTradingStrategiesInStocks.pdf Applying Deep Learning To Enhance Momentum Trading Strategies In Stocks] | ||
| + | |||
| + | (2016) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305214717_High-Frequency_Trading_Strategy_Based_on_Deep_Neural_Networks | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://people.idsia.ch/~juergen/finance.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Hinton's SCIENCE paper: [https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/science.pdf Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks] == | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/aurofable/18551_Project/tree/master/rough/nn/Martin_Web_Autoencoder MATLAB | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/dustinstansbury/medal MATLAB | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/joncox123/Cortexsys MATLAB/GPU | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/lajanugen/RBM-Autoencoder PYTHON/Theano | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/Lapulatos/AutoEncoder JAVA | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/Cospel/rbm-ae-tf Python/TF | ||
== S/W == | == S/W == | ||
[http://playground.tensorflow.org http://playground.tensorflow.org] | [http://playground.tensorflow.org http://playground.tensorflow.org] | ||
| − | [https://github.com/p-i-/SwiftNet SwiftNet] <-- My own back propagating NN (in Swift) | + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wuo4JdG3SvU&list=PL9Hr9sNUjfsmEu1ZniY0XpHSzl5uihcXZ TensorFlow in IPython YouTube] (5 vids) |
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/p-i-/SwiftNet SwiftNet] <-- My own back propagating NN (in Swift) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Stats Courses == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLFDbGp5YzjqXQ4oE4w9GVWdiokWB9gEpm OxEduc: Bayesian statistics: a comprehensive course] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a_08GKWHFWo Gibbs Sampling -- Niemi] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Blogs etc. == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Otoro: http://blog.otoro.net/2016/04/01/generating-large-images-from-latent-vectors/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Colah: http://colah.github.io/posts/2014-03-NN-Manifolds-Topology/ <-- Pics of manifolds! | ||
| + | |||
| + | Karpathy: http://karpathy.github.io/2016/05/31/rl/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Brandon Amos: https://bamos.github.io/2016/08/09/deep-completion/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Miriam: http://blog.fastforwardlabs.com/2016/08/12/introducing-variational-autoencoders-in-prose-and.html | ||
== Misc == | == Misc == | ||
| Line 38: | Line 146: | ||
Links: https://github.com/memo/ai-resources | Links: https://github.com/memo/ai-resources | ||
| − | http:// | + | http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/ |
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gfPUWwBkXZY <-- Hopfield vid | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www.gitxiv.com/ <-- Amazing projects here! | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/ChristosChristofidis/awesome-deep-learning <-- MANY ML Links! | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://blog.keras.io/building-autoencoders-in-keras.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://videolectures.net/cyberstat2012_friston_free_energy/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | ----- | ||
| + | ----- | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Boltzmann Machines = | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hopfield to Boltzmann http://haohanw.blogspot.co.uk/2015/01/boltzmann-machine.html which links to http://arxiv.org/pdf/1510.04781v2.pdf | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hinton's Lecture, then: | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boltzmann_machine | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Boltzmann_machine | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/absps/guideTR.pdf Hinton (2010) -- A Practical Guide to Training Restricted Boltzmann Machines] | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242509302_Learning_and_relearning_in_Boltzmann_machines | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://image.diku.dk/igel/paper/AItRBM-proof.pdf An Introduction to Restricted Boltzmann Machines] (hard) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://blog.echen.me/2011/07/18/introduction-to-restricted-boltzmann-machines/ Edwin Chen -- Python RBM] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boltzmann_distribution Boltzmann Distribution] ==== | ||
| + | Consider this 'background'. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Suppose you have some system being held in thermal equilibrium by a heat-bath. Now suppose the system has a finite number of possible states. Like a 3x3x3 cm cube containing molecules with total KE 900J, and the states are: {first 1x1x1 zone has 999J, next has 1, others have 0} (very unlikely), {998,1,1,0,...}, etc. Notice we are making (two) artificial discretisation(s). So let's think of the whole cube as the reservoir/heat-bath and the middle 1x1x1 cm zone as our system. (better would be to make our reservoir much larger e.g. 101x101x101 in proportion to our system -- think infinite). | ||
| + | |||
| + | We would expect our system to fluctuate around 100J. We can ask: what is the probability our system has 97J at a given moment? Boltzmann figured out that if you know the energy of a particular state you can figure out the probability the system is in that state: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(s) \propto e^{-kE_s}</math> where <math>E_s</math> is the energy for that state. | ||
| + | |||
| + | So we can write: <math>P(s) = \frac{1}{Z}e^{-kE_s}</math> where <math>Z</math> is the PARTITION FUNCTION (energy summed over all possible states). | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you graph the energy (X axis) vs probability {system has that energy} (Y axis) you have a '''Boltzmann Distribution'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Susskind derives this [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SmmGDn8OnTA here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/159846/why-is-the-energy-and-the-probability-of-a-configuration-related-in-a-boltzmann | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Boltzmann MACHINE === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Cycle.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | A Boltzmann Machine is a Hopfield Net, but each neuron stochastically has state 0 or 1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | So, imagine a 12 point mystic rose: 3 hidden units, 9 visible units. You can visualise the weights between each pair of units by the thickness of that line if you like. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Retrieval:''' First imagine the network is already trained to recognise 3 simple shapes, i.e. suppose weights are fixed in such a way that input vectors 111-000-000, 000-111-000 and 000-000-111 generate basins i.e. minima of low network energy (network energy is just the sum of active synapses. So <math>\sum w_{ij}</math> where i,j both on). | ||
| + | |||
| + | So, '''CLAMP''' visible units to 111-100-000, set the 3 hidden units to random binary & keep randomly choosing a neuron and updating its state (0 or 1) by some probabilistic logic that will guarantee our system eventually settles down into a Boltzmann distribution, i.e. reaches thermal equilibrium. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This will mean that with high probability it will be in a low energy state. Think: place a marble nearby & it will roll to the nearest basin. So we should be able to recover 000-111-000. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :'''Now let's cook up that updating logic.''' | ||
| + | :It looks like Wikipedia's approach [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boltzmann_machine#Probability_of_a_unit.27s_state here] is to suppose the system is already in a Boltzmann distribution & we wish to update it in a way that it is still in a Boltzmann distribution afterwards: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::We can calculate the probability of a given unit's state being ON just by knowing the system's energy gap between that unit being ON and OFF: | ||
| + | ::<math>p_\text{i=on} = \frac{1}{1+\exp(-\frac{\Delta E_i}{T})}</math> where <math>\Delta E_i = E_\text{i=off} - E_\text{i=on}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Yup that's a good ole Sigmoid! And it should be simple to get that Energy delta just by figuring out the expected Energy contribution of that neuron. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ----- | ||
| + | |||
| + | That demonstrates its ''retrieval'' ability. But how about its '''storage''' ability? | ||
| + | |||
| + | i.e. If you feed in those three training images, we need some way of twiddling the weights to create 3 appropriate basins. i.e. We want the network to have ultralow energy for those 3 input vectors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | So you want to perform some kind of gradient descent: figure out the rate at which the energy is decreasing as you twiddle your weight. And adjust the weight to get maximum energy ''decrease''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hinton describes this process on Scholarpedia: [http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Boltzmann_machine#Learning_in_Boltzmann_machines Learning in Boltzmann machines]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \bigg\langle \frac{\partial \log P(\mathbf{v})}{\partial w_{ij}} \bigg\rangle_\mathrm{data} = | ||
| + | \langle s_i s_j \rangle_\mathrm{data} - \langle s_i s_j \rangle_\mathrm{model} = \Delta | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Actually is there a simpler way to think of this? The RHS is just the elevation of synapse-load (for this particular synapse) (or 'fire-together' if you like) during training over the same during 'dreaming'. So we want to 'wire-together' in proportion to 'fire together'. This is good ole Hebbian Learning. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now since <math> E \propto \log P </math>, we have <math> \bigg\langle\frac{\Delta E}{\Delta w_{ij}}\bigg\rangle _\mathrm{data} = \Delta</math> which we can write <math> \frac{\langle\Delta E\rangle_\mathrm{data}}{\Delta w_{ij}} = \Delta</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | i.e. <math>\Delta E ~ \Delta w_{ij} \times \Delta</math> ... struggling to finish this. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ----- | ||
| + | |||
| + | = RBM Code = | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/237373/architecture-of-salakhudinovs-dbm-code <-- Salakh (2010?) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Hinton (2006)''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://science.sciencemag.org/content/suppl/2006/08/04/313.5786.504.DC1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/science.pdf | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/MatlabForSciencePaper.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | ----- | ||
| + | |||
| + | = DBN etc. = | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/dfdx/Boltzmann.jl <-- DBN in Julia | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.quora.com/What-is-an-intuitive-explanation-of-the-wake-sleep-algorithm | ||
| + | |||
| + | RWS (Reweighted Wake-Sleep) -- https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2751 https://github.com/jbornschein/reweighted-ws/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | DARN -- Deep AutoRegressive Networks -- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1310.8499.pdf | ||
| + | |||
| + | NADE -- http://www.dmi.usherb.ca/~larocheh/projects_nade.html https://github.com/prashanthpai/NADE | ||
| + | |||
| + | NADE-k -- https://github.com/yaoli/nade_k https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.1485 | ||
| + | |||
| + | MADE -- https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03509 https://github.com/mgermain/MADE/releases/tag/ICML2015 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ^ autoregressive property: xOut_k depends only on xIn_{1 to k-1} | ||
| + | |||
| + | = GAN = | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://wiseodd.github.io/techblog/2016/09/17/gan-tensorflow/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www.inference.vc/my-summary-of-adversarial-training-nips-workshop/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HN9NRhm9waY Ian Goodfellow on #AIWTB], [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RvgYvHyT15E&t=476s NIPS talk] is better I think! | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.00160 NIPS 2016 Tutorial] (60 pages!) | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Variational Autoencoders = | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://kvfrans.com/variational-autoencoders-explained/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://jaan.io/what-is-variational-autoencoder-vae-tutorial/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.05908.pdf Tutorial on Variational Autoencoders] | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://blog.fastforwardlabs.com/2016/08/12/introducing-variational-autoencoders-in-prose-and.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Bayesian Deep Learning = | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://bayesiandeeplearning.org/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | -> [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FD8l2vPU5FY NIPS 2016 KeyNote: History of Bayesian Neural Networks] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Julia = | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://juliaml.github.io/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/svaksha/Julia.jl/blob/master/AI.md | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/sphinxteam/Boltzmann.jl <-- DBN here | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Optimization = | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://sebastianruder.com/optimizing-gradient-descent/ <-- Nice animations showing the effectiveness of various optimisers | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www.breloff.com/JuliaML-and-Plots/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://github.com/JuliaML/StochasticOptimization.jl | ||
| + | |||
| + | ADAM https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980v8.pdf | ||
| + | |||
| + | ADAM + Nesterov http://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2015/054_report.pdf | ||
Latest revision as of 01:55, 21 April 2017
Deep Learning Papers Reading Roadmap
Contents
[hide]- 1 Communities
- 2 Getting Started
- 3 Tuts
- 4 Other courses
- 5 RL
- 6 Books
- 7 Trading
- 8 Hinton's SCIENCE paper: Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks
- 9 S/W
- 10 Stats Courses
- 11 Blogs etc.
- 12 Misc
- 13 Boltzmann Machines
- 14 RBM Code
- 15 DBN etc.
- 16 GAN
- 17 Variational Autoencoders
- 18 Bayesian Deep Learning
- 19 Julia
- 20 Optimization
Communities
IRC FreeNode: ##machinelearning
Getting Started
DeepLearning.TV YouTube playlist -- good starter!
Keras runs on top of TensorFlow or Theano
Tuts
http://brohrer.github.io/how_bayesian_inference_works.html <-- good ML vids too
UFLDL Stanford (Deep Learning) Tutorial
Principles of training multi-layer neural network using backpropagation <-- Great visual guide!
http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/ <-- Python code here (Theano)
(Coursera) Neural Networks for Machine Learning — Hinton
- Hinton's homepage
- Coursera course - Intro vid for course - Vids (on YouTube) - same, better organized
- Bayesian Nets Tutorial -- helpful for later parts of Hinton
Code:
- https://github.com/bpjsincl/coursera-neural-net <-- Python - https://github.com/BradNeuberg/hinton-coursera <-- MatLab - https://github.com/davidandrzej/py-coursera-neural <-- no good - https://github.com/Sohojoe/hinton-coursera <-- fork of the Matlab
- https://github.com/mdenil/dropout
- http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/code.html <-- Boltzmann stuff MATLAB Ruslan Salakhutdinov and Geoff Hinton - https://github.com/echen/restricted-boltzmann-machines Python RBM NICE - http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/rbm.html - http://deeplearning4j.org/restrictedboltzmannmachine.html - Hinton, Salakhutdinov (2006) -- Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks <-- Stacked RBM AutoEncoders (DBM) + CODE!
Exercises:
- https://www.reddit.com/r/MachineLearning/comments/1wgleb/where_can_i_find_the_exercises_to_the_coursera_ml/
Other courses
Deep learning at Oxford 2015 (Nando de Freitas)
Notes for Andrew Ng's Coursera course.
Hugo Larochelle: Neural networks class - Université de Sherbrooke RESOURCES
Karpathy -- CS231n: course here, http://karpathy.github.io/neuralnets/
RL
David Silver's RL course YouTube playlist
http://rll.berkeley.edu/deeprlcourse/
https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-best-books-about-reinforcement-learning
Books
Nielsen -- Neural Networks and Deep Learning <-- online book
Rojas (1996) -- Neural Networks - A Systematic Introduction ???
The Elements of Statistical Learning
Book-like Papers:
On the Origin of Deep Learning
Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview
Trading
(2013) Applying Deep Learning To Enhance Momentum Trading Strategies In Stocks
http://people.idsia.ch/~juergen/finance.html
Hinton's SCIENCE paper: Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks
https://github.com/aurofable/18551_Project/tree/master/rough/nn/Martin_Web_Autoencoder MATLAB
https://github.com/dustinstansbury/medal MATLAB
https://github.com/joncox123/Cortexsys MATLAB/GPU
https://github.com/lajanugen/RBM-Autoencoder PYTHON/Theano
https://github.com/Lapulatos/AutoEncoder JAVA
https://github.com/Cospel/rbm-ae-tf Python/TF
S/W
http://playground.tensorflow.org
TensorFlow in IPython YouTube (5 vids)
SwiftNet <-- My own back propagating NN (in Swift)
Stats Courses
OxEduc: Bayesian statistics: a comprehensive course
Blogs etc.
Otoro: http://blog.otoro.net/2016/04/01/generating-large-images-from-latent-vectors/
Colah: http://colah.github.io/posts/2014-03-NN-Manifolds-Topology/ <-- Pics of manifolds!
Karpathy: http://karpathy.github.io/2016/05/31/rl/
Brandon Amos: https://bamos.github.io/2016/08/09/deep-completion/
Miriam: http://blog.fastforwardlabs.com/2016/08/12/introducing-variational-autoencoders-in-prose-and.html
Misc
Links: https://github.com/memo/ai-resources
http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gfPUWwBkXZY <-- Hopfield vid
http://www.gitxiv.com/ <-- Amazing projects here!
https://github.com/ChristosChristofidis/awesome-deep-learning <-- MANY ML Links!
https://blog.keras.io/building-autoencoders-in-keras.html
http://videolectures.net/cyberstat2012_friston_free_energy/
Boltzmann Machines
Hopfield to Boltzmann http://haohanw.blogspot.co.uk/2015/01/boltzmann-machine.html which links to http://arxiv.org/pdf/1510.04781v2.pdf
Hinton's Lecture, then:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boltzmann_machine
http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Boltzmann_machine
Hinton (2010) -- A Practical Guide to Training Restricted Boltzmann Machines
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242509302_Learning_and_relearning_in_Boltzmann_machines
An Introduction to Restricted Boltzmann Machines (hard)
Boltzmann Distribution
Consider this 'background'.
Suppose you have some system being held in thermal equilibrium by a heat-bath. Now suppose the system has a finite number of possible states. Like a 3x3x3 cm cube containing molecules with total KE 900J, and the states are: {first 1x1x1 zone has 999J, next has 1, others have 0} (very unlikely), {998,1,1,0,...}, etc. Notice we are making (two) artificial discretisation(s). So let's think of the whole cube as the reservoir/heat-bath and the middle 1x1x1 cm zone as our system. (better would be to make our reservoir much larger e.g. 101x101x101 in proportion to our system -- think infinite).
We would expect our system to fluctuate around 100J. We can ask: what is the probability our system has 97J at a given moment? Boltzmann figured out that if you know the energy of a particular state you can figure out the probability the system is in that state:
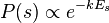 where
where 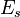 is the energy for that state.
is the energy for that state.
So we can write: 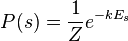 where
where 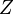 is the PARTITION FUNCTION (energy summed over all possible states).
is the PARTITION FUNCTION (energy summed over all possible states).
If you graph the energy (X axis) vs probability {system has that energy} (Y axis) you have a Boltzmann Distribution.
Susskind derives this here.
Boltzmann MACHINE
A Boltzmann Machine is a Hopfield Net, but each neuron stochastically has state 0 or 1.
So, imagine a 12 point mystic rose: 3 hidden units, 9 visible units. You can visualise the weights between each pair of units by the thickness of that line if you like.
Retrieval: First imagine the network is already trained to recognise 3 simple shapes, i.e. suppose weights are fixed in such a way that input vectors 111-000-000, 000-111-000 and 000-000-111 generate basins i.e. minima of low network energy (network energy is just the sum of active synapses. So 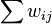 where i,j both on).
where i,j both on).
So, CLAMP visible units to 111-100-000, set the 3 hidden units to random binary & keep randomly choosing a neuron and updating its state (0 or 1) by some probabilistic logic that will guarantee our system eventually settles down into a Boltzmann distribution, i.e. reaches thermal equilibrium.
This will mean that with high probability it will be in a low energy state. Think: place a marble nearby & it will roll to the nearest basin. So we should be able to recover 000-111-000.
- Now let's cook up that updating logic.
- It looks like Wikipedia's approach here is to suppose the system is already in a Boltzmann distribution & we wish to update it in a way that it is still in a Boltzmann distribution afterwards:
- We can calculate the probability of a given unit's state being ON just by knowing the system's energy gap between that unit being ON and OFF:
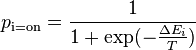 where
where 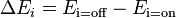
- Yup that's a good ole Sigmoid! And it should be simple to get that Energy delta just by figuring out the expected Energy contribution of that neuron.
That demonstrates its retrieval ability. But how about its storage ability?
i.e. If you feed in those three training images, we need some way of twiddling the weights to create 3 appropriate basins. i.e. We want the network to have ultralow energy for those 3 input vectors.
So you want to perform some kind of gradient descent: figure out the rate at which the energy is decreasing as you twiddle your weight. And adjust the weight to get maximum energy decrease.
Hinton describes this process on Scholarpedia: Learning in Boltzmann machines.
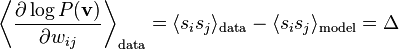
Actually is there a simpler way to think of this? The RHS is just the elevation of synapse-load (for this particular synapse) (or 'fire-together' if you like) during training over the same during 'dreaming'. So we want to 'wire-together' in proportion to 'fire together'. This is good ole Hebbian Learning.
Now since 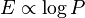 , we have
, we have 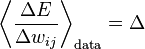 which we can write
which we can write 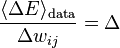
i.e. 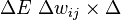 ... struggling to finish this.
... struggling to finish this.
RBM Code
http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/237373/architecture-of-salakhudinovs-dbm-code <-- Salakh (2010?)
Hinton (2006)
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/suppl/2006/08/04/313.5786.504.DC1
https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/science.pdf
http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/MatlabForSciencePaper.html
DBN etc.
https://github.com/dfdx/Boltzmann.jl <-- DBN in Julia
https://www.quora.com/What-is-an-intuitive-explanation-of-the-wake-sleep-algorithm
RWS (Reweighted Wake-Sleep) -- https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2751 https://github.com/jbornschein/reweighted-ws/
DARN -- Deep AutoRegressive Networks -- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1310.8499.pdf
NADE -- http://www.dmi.usherb.ca/~larocheh/projects_nade.html https://github.com/prashanthpai/NADE
NADE-k -- https://github.com/yaoli/nade_k https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.1485
MADE -- https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03509 https://github.com/mgermain/MADE/releases/tag/ICML2015
^ autoregressive property: xOut_k depends only on xIn_{1 to k-1}
GAN
http://wiseodd.github.io/techblog/2016/09/17/gan-tensorflow/
http://www.inference.vc/my-summary-of-adversarial-training-nips-workshop/
Ian Goodfellow on #AIWTB, NIPS talk is better I think!
NIPS 2016 Tutorial (60 pages!)
Variational Autoencoders
http://kvfrans.com/variational-autoencoders-explained/
https://jaan.io/what-is-variational-autoencoder-vae-tutorial/
Tutorial on Variational Autoencoders
http://blog.fastforwardlabs.com/2016/08/12/introducing-variational-autoencoders-in-prose-and.html
Bayesian Deep Learning
http://bayesiandeeplearning.org/
-> NIPS 2016 KeyNote: History of Bayesian Neural Networks
Julia
https://github.com/svaksha/Julia.jl/blob/master/AI.md
https://github.com/sphinxteam/Boltzmann.jl <-- DBN here
Optimization
http://sebastianruder.com/optimizing-gradient-descent/ <-- Nice animations showing the effectiveness of various optimisers
http://www.breloff.com/JuliaML-and-Plots/
https://github.com/JuliaML/StochasticOptimization.jl
ADAM https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980v8.pdf
ADAM + Nesterov http://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2015/054_report.pdf
